The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming our world, creating a network of smart, interconnected devices. From homes to industries, IoT is changing how we interact with our environment and process information. While it promises to revolutionize various sectors and improve daily life, IoT also presents challenges in security and privacy that must be addressed as we embrace this new era of connectivity.
Understanding the Basics of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the vast network of interconnected, internet-enabled devices that collect, transmit, and exchange data. These smart objects range from everyday household items to sophisticated industrial equipment. At its core, IoT is about extending internet connectivity beyond traditional devices like computers and smartphones to a diverse array of physical objects.
Connected devices in the IoT ecosystem are equipped with sensors, processors, and communication hardware that allow them to gather and share information. This enables machine-to-machine communication, where devices can interact and make decisions without human intervention. Examples of IoT devices include smart thermostats, wearable fitness trackers, connected cars, and industrial sensors.
The power of IoT lies in its ability to create a more efficient, responsive, and data-driven world. By connecting previously isolated objects to the internet, IoT facilitates real-time monitoring, analysis, and automation across various sectors. This technology is transforming industries, enhancing consumer experiences, and paving the way for innovative solutions to complex problems in areas such as healthcare, agriculture, and urban planning.
The Core Components of IoT Systems
IoT systems are composed of several key components that work together to collect, transmit, and analyze data from the physical world. At the heart of these systems are IoT sensors, which gather information about the environment, such as temperature, humidity, or motion. These sensors are often paired with actuators, devices that can perform actions based on the data received, like adjusting thermostats or turning on lights.
Connectivity is crucial in IoT systems, enabling devices to communicate with each other and transmit data to central hubs. This is achieved through various wireless technologies, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and specialized IoT protocols like LoRaWAN or Zigbee.
Data processing is another vital component, involving the analysis and interpretation of the vast amounts of information collected by IoT devices. This can occur at different levels, including edge computing, where data is processed closer to the source for faster response times, and cloud computing, which provides scalable resources for more complex analytics and long-term storage.
Cloud computing platforms play a significant role in IoT systems, offering powerful tools for data management, visualization, and machine learning. These platforms enable businesses to derive meaningful insights from their IoT data and make informed decisions based on real-time information.
By integrating these core components, IoT systems create a seamless flow of information from the physical world to digital platforms, enabling innovative applications across various industries and improving efficiency in countless processes.
How IoT Devices Communicate and Share Data
IoT devices rely on various wireless protocols to communicate and share data effectively. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology enables short-range communication, often used in inventory tracking and access control systems. Bluetooth, with its low energy consumption, is ideal for personal area networks and connecting devices like smartwatches to smartphones.
Wi-Fi is a popular choice for home and office IoT devices, offering high-speed data transfer and the ability to connect multiple devices simultaneously. For long-range communication, cellular networks (3G, 4G, and emerging 5G) provide extensive coverage, allowing IoT devices to transmit data over vast distances.
IoT platforms act as central hubs, collecting and processing data from multiple devices. These platforms enable device management, data analysis, and integration with other systems, forming the backbone of IoT ecosystems. As the IoT landscape evolves, new protocols and communication methods continue to emerge, enhancing the efficiency and capabilities of connected devices.
The Role of Big Data and AI in IoT
Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) play a crucial role in unlocking the full potential of the Internet of Things (IoT). As IoT devices continuously generate vast amounts of data, advanced data analytics techniques are employed to extract meaningful insights. Machine learning algorithms process this data, identifying patterns and trends that would be impossible for humans to discern manually.
AI-powered systems can analyze real-time data streams from IoT sensors, enabling predictive maintenance in various industries. This proactive approach helps prevent equipment failures, reduce downtime, and optimize operational efficiency. Furthermore, AI algorithms can adapt and improve their performance over time, leading to increasingly accurate predictions and recommendations.
The synergy between Big Data, AI, and IoT facilitates smart decision-making across diverse sectors. For instance, in smart cities, AI-driven systems can analyze traffic patterns, energy consumption, and public safety data to optimize resource allocation and improve urban living conditions. In healthcare, AI-powered IoT devices can monitor patients’ vital signs, predict potential health issues, and alert medical professionals when intervention is necessary.
As these technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated applications that leverage the power of Big Data and AI to enhance IoT capabilities, ultimately leading to more efficient, sustainable, and interconnected systems.
Real-World Applications of IoT Technology
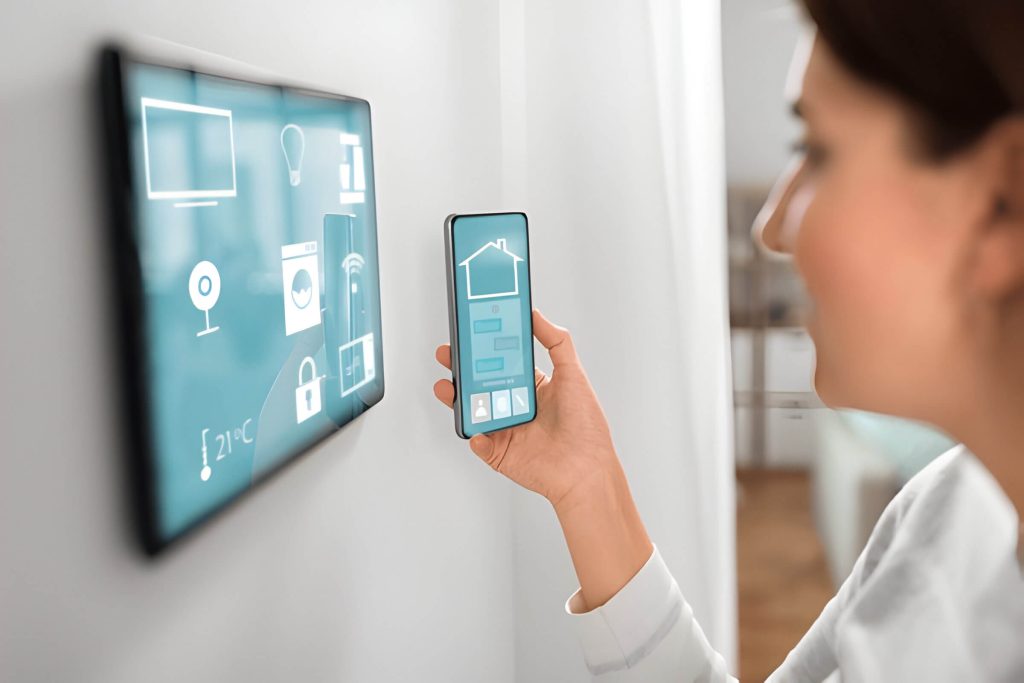

The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized various sectors, offering innovative solutions to everyday challenges. Smart homes represent one of the most visible applications, allowing homeowners to control lighting, temperature, and security systems remotely. In the industrial sphere, IoT has transformed manufacturing processes, enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing production efficiency.
Connected cars have become a reality, with vehicles now equipped with sensors and communication systems that enhance safety, navigation, and entertainment. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, have gained popularity by providing real-time health monitoring and personalized fitness recommendations.
Smart cities leverage IoT technology to improve urban living, implementing solutions for traffic management, waste collection, and energy conservation. In agriculture, IoT applications are enhancing crop yields and resource management through precision farming techniques, soil sensors, and automated irrigation systems.
As IoT technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications across various industries, further integrating our physical and digital worlds.
Security and Privacy Concerns in IoT
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, security and privacy concerns have become paramount. IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal and sensitive data, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. To address these risks, robust security measures are essential.
Data protection in IoT starts with encryption. Implementing strong encryption protocols ensures that information transmitted between devices and servers remains confidential and tamper-proof. Additionally, device authentication mechanisms help prevent unauthorized access and protect against man-in-the-middle attacks.
Privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, play a crucial role in governing how IoT companies handle user data. Compliance with these regulations is not only legally necessary but also builds trust with consumers. IoT manufacturers and service providers must prioritize data minimization, user consent, and transparent data practices.
Another critical aspect of IoT security is regular software updates and patch management. As new vulnerabilities are discovered, timely updates can protect devices from emerging threats. Manufacturers should design IoT devices with security in mind, incorporating features like secure boot processes and hardware-based security elements.
As the IoT ecosystem grows more complex, a multi-layered approach to security becomes increasingly important. This includes securing individual devices, network communications, and cloud infrastructure. By addressing security and privacy concerns proactively, the IoT industry can build a more trustworthy and resilient ecosystem for the future.
The Future of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to evolve rapidly, shaping our digital landscape and transforming various industries. As we look ahead, several key trends and predictions emerge for the future of IoT:
5G and IoT: The rollout of 5G networks will significantly enhance IoT capabilities, enabling faster data transmission, lower latency, and increased device connectivity. This synergy will unlock new possibilities for real-time applications and more sophisticated IoT ecosystems.
Edge Computing: As IoT devices generate massive amounts of data, edge computing will play a crucial role in processing information closer to the source. This approach reduces latency, enhances security, and optimizes bandwidth usage, making IoT applications more efficient and responsive.
IoT Standardization: Efforts towards standardization in IoT protocols and platforms will intensify, fostering better interoperability between devices and systems. This standardization will facilitate seamless integration and communication across diverse IoT ecosystems.
IoT and Blockchain: The integration of blockchain technology with IoT will enhance security, transparency, and trust in IoT networks. This combination will enable secure data sharing, automated smart contracts, and improved traceability in supply chains and other IoT-driven processes.
Sustainable IoT: As environmental concerns grow, the focus on sustainable IoT solutions will increase. This includes developing energy-efficient devices, implementing circular economy principles in IoT hardware, and leveraging IoT for environmental monitoring and conservation efforts.
These trends indicate a future where IoT becomes more pervasive, efficient, and integral to our daily lives and business operations. As the technology matures, we can expect to see innovative applications across various sectors, from smart cities and healthcare to agriculture and manufacturing.